Data on demand is a Redox repository that ingests and stores data from systems that only support asynchronous, push-based data exchange. This allows you to perform synchronous queries to retrieve specific data when you need it, avoiding the overhead of processing and storing a high volume of unnecessary messages.
However, you might want to use data on demand with Redox FHIR® queries instead of our Redox data models. This article explains what you need to be aware of if you want to use FHIR® instead of our standard offering of data on demand.
There are three typical configurations for FHIR® data on demand:
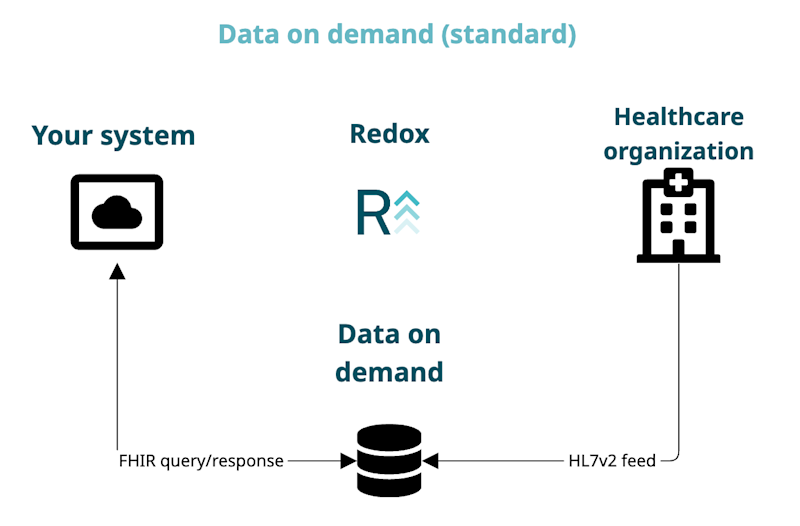
- Data on demand (standard): You query the Redox repository for data when you need it.
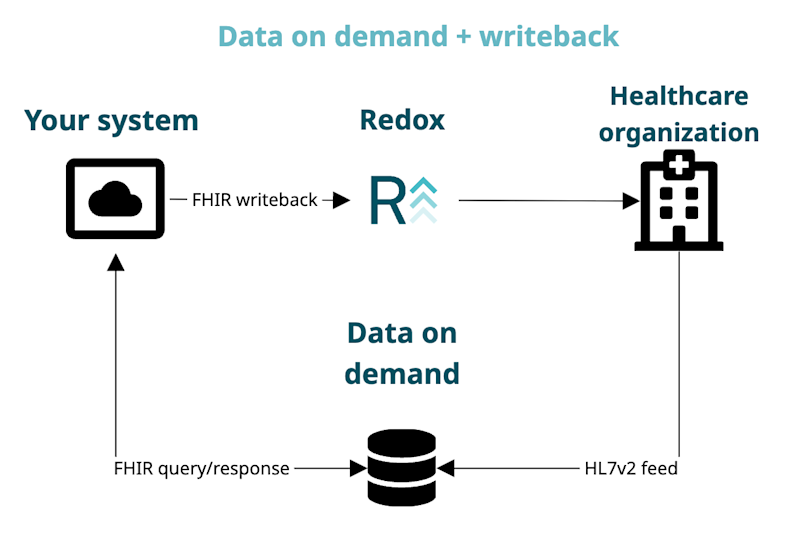
- Data on demand + writeback: You query the Redox repository, and you can also send data back to the EHR system with a writeback operation.
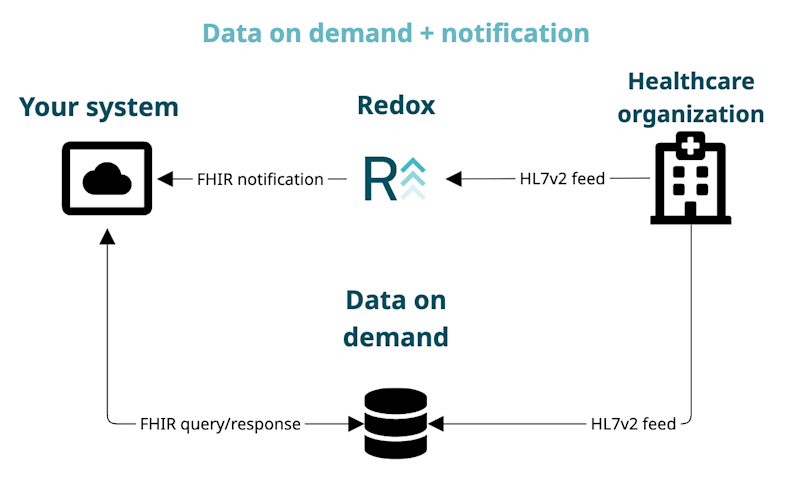
- Data on demand + notification: You receive a lightweight notification, which you use as a trigger to query the Redox repository for full details.
Alternatively, you might find that polling is a better option for you, depending on your system and your connection’s capabilities. Learn about polling. We can help you decide whether data on demand or polling might suit your system the best based on your unique integrations.
Using Redox FHIR® with data on demand saves you time by simplifying the amount of effort needed to consume the HL7v2 data directly. Instead, a Redox FHIR® server ingests your connection’s data into a data on demand repository. Then, you can query for your connection’s data from Redox. Learn more about our standard data on demand configuration.
With data on demand, you can query the repository, but you typically can’t write back to it to update your connection’s system. However, it’s possible to write data back to your connection using a FHIR® writeback operation (a form of FHIR® messaging). Learn more about messaging.
For an HL7v2 subscription with an EHR system, the data you write back eventually ends up in the data on demand repository after the EHR system processes the message. You can do this if you want to rely on the EHR system as the ultimate source of truth. It works, so long as you allow time for the EHR system to mediate and validate the data before it gets to your data on demand repository.
For example, let’s say you create a patient record and send it back to the EHR system. But the EHR system already has a record for that patient. While processing the new record you send, the EHR system might merge the patient records. After processing is complete, you could query for that patient, knowing that the EHR system is the source of truth.
Another potential data on demand configuration relies on notifications to trigger your workflow.
Let’s say you listen for notifications from your connection. This means that a healthcare organization sends a message to your system whenever there’s a relevant update. When you receive this notification, you can query your data on demand repository for more information.
For example, if you receive a notification that a patient was discharged from the hospital, you could retrieve a transition of care document to get details about their inpatient stay.