To search for patient records, you first need to identify organizations that have seen your patient. Then you can request patient documents from each of those organizations.
If you want to know where you can get patient records from, explore a list of active Carequality participants.
You can also check out test patient data for context on the code examples we provide or for your own testing.
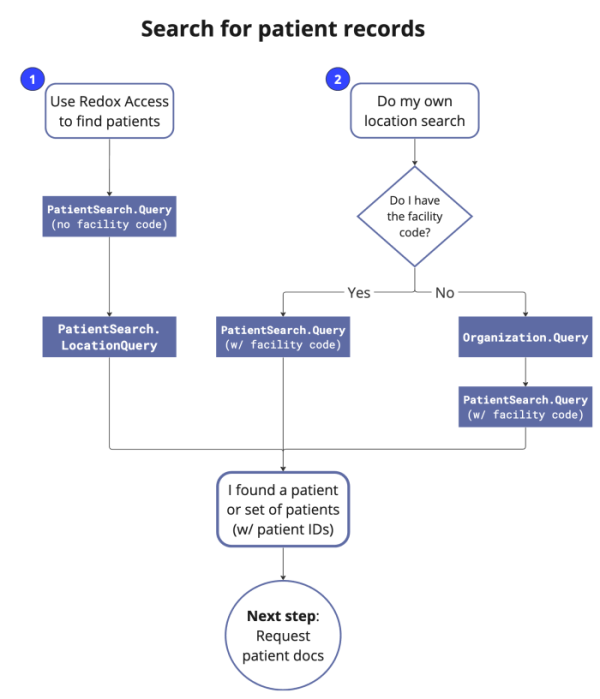
You have two options for finding a patient’s record:
- Search for a patient using Redox Access: If you don’t know where the patient's located or if the patient exists in multiple locations, Redox Access can provide a list of possibilities with its record locator service. This is the most common option since it allows you to identify all of the organizations where a patient’s record may exist.
- Search for a patient with your own location search: There are two ways to perform your own location search, depending on whether you have the facility code(s). You can perform this type of search with either the Redox Data Model API or the Redox FHIR® API.
- If you have a static list of locations you wish to search or know exactly which organizations have records for the patient, you can search those specific organizations or locations directly. For this option, you must already know the facility code(s). Also, keep in mind that you can only search one organization at a time.
- If you don't know where the patient's records exist, you could search for relevant organizations first. You could use parameters like ZIP code or radius around the patient's address to find a list of options. The response returns a list of matching organization(s) with their facility code(s). Then, you can perform a patient search like in the first option.
Regardless of the patient search option you use, each query contains required metadata fields that identify the requesting user and their organization, specify the purpose of use, and direct the request to the target organization. These fields exist within the Meta section of the query.
You must populate any test requests with the appropriate destination ID in the Meta.Destinations array based on the environment and type of requests:
| Request purpose | Staging ID | Production ID |
|---|---|---|
| Search for a patient with Redox Access | adf917b5-1496-4241-87e2-ed20434b1fdb | 97f2dc1d-c71b-43a7-a436-9b789d44c804 |
| Search for a patient within a specific organization | 1ca254a8-8d42-4593-abb4-b21399d9de57 | 6391b961-55ae-430b-a789-cf575f03fca0 |
| Query for/create/update/delete an organization | a07afe3b-d247-4415-827f-6837707e1b8b | 5d0fd248-6c52-4ad9-b907-ae10bf2dcc39 |
| Search for a clinical summary/document | ec745338-8849-43ad-a7ce-4bc5bf1d8b89 | 628cbf79-1156-4923-b9d0-285906160ed6 |
| Save patient details and documents to your repository | This is specific to your org. Redox provides the correct ID. | This is specific to your org. Redox provides the correct ID. |
This popular option relies on Redox Access's record locator service to do the heavy lifting for you. Record locator service looks for your patient's record at Carequality participant facilities within the same areas as your organization and the patient's home address (if supplied). Record locator service also leverages results from other Redox client searches so we can go beyond the search area, if possible.
- If you already have the network patient ID, you can skip to step 3. If you don't have the network patient ID, using Postman or curl, send a PatientSearch.Query request with the patient's demographics to the Redox gateway (2.16.840.1.113883.3.6147.458.2).What demographic information to includeExample: Search for a patientbashAPI reference
- Record locator services takes the patient's demographics and returns the network patient ID.
- Using Postman or curl, send a PatientSearch.LocationQuery request with the network patient ID to the record locator destination (adf917b5-1496-4241-87e2-ed20434b1fdb for staging requests; 97f2dc1d-c71b-43a7-a436-9b789d44c804 for production requests).Example: Search for locationsbashAPI reference
- The response returns a list of locations where the patient exists—along with the patient’s localized IDs at each location, which we validate.Example: Successful response for location searchjson
The Meta.Extensions.task-status.string field contains a status of either Active or Success.
Status | Definition | Results |
|---|---|---|
Active | The process is asynchronously collecting locations. | The Patients array populates with any partial results as they become available. |
Success | The process has finished and all possible locations were found. | Any available results have been returned. If the Patients array is empty, it means no patients were found. |
The response waits up to 10 seconds to reach a Success state. If unable to reach Success in that time, the response retains an Active status. You can retry the exact request repeatedly until it reaches a Success state.
If you know exactly where a patient was seen previously, you can search for a patient at an individual organization. If you want to search multiple organizations, you must search them one at a time.
- If you already have an organization and its respective OID to search, you can skip to step 4. If you don’t have an OID for the organization you want to search, send the Organization.Query request. With this query, you search by ZIP code radius or organization name.Example: Search for organizationsbashAPI reference
- If the request is successful, you receive a synchronous Organization.QueryResponse with the relevant organization results.Example: Successful response for organization searchjson
- From the results list, you can select one or all of these organizations to then run a patient search.
- Now that you have an organization to search, send the PatientSearch.Query request with the patient's demographics to see if that organization has your patient’s records. You must use the organization’s OID in each request.Where to find the OIDData model example: Search for a patient within one organizationbashAPI referenceFHIR example: Search for a patient within one organizationbashFHIR API reference
- If your search matches a patient at the given organization, the response returns the patient’s identifier and additional details.Data model example: Successful response for a patient search within one organizationjsonIf a patient isn’t found, the response returns an empty array.FHIR example: Successful response for a patient search within one organizationjson
- Repeat steps 4 and 5 for every organization you want to search.